(719 products available)
























































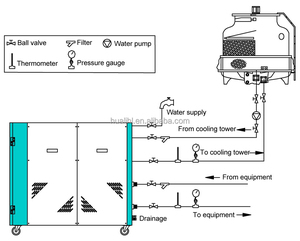




























































































































































Absorption chillers are classified into several different types based on various factors, including the working principle, the refrigerant absorption process, and the type of refrigerant.
Lithium bromide absorption chiller: It is one of the most widely used absorption chillers on the market. The lithium bromide absorption chiller uses water as a refrigerant and lithium bromide as an absorbent to produce cooling. It is mainly composed of a generator, absorber, evaporator, and condenser. Lithium bromide absorption chillers are also divided into two types according to the working principle: single-effect and double-effect chillers. The former can produce one unit of refrigeration from each unit of heat energy, while the latter can generate two units of refrigeration from each unit of heat energy.
Single-effect absorption chiller: It is the simplest type. The single-effect absorption chiller uses a single absorber and generator to create a cooling effect from a heat source. It is an economical and efficient method to provide cooling solutions for various applications.
Double-effect absorption chiller: It employs two generators, which increases system efficiency and more cooling capacity. The double-effect absorption chiller produces more refrigeration per unit of heat input compared to the single-effect unit.
Triple-effect absorption chiller: It is also known as a multiple-effect absorption chiller. The triple-effect absorption chiller is more efficient than the single-effect and double-effect models. It utilizes three generators to create additional cooling capacity. The triple-effect absorption chiller is ideal for large-scale industrial and commercial applications that require high refrigeration output and energy efficiency.
Direct-fired absorption chiller: It directly burns natural gas or other fuels to provide the required heat for the absorption refrigeration process, making it more efficient. The direct-fired absorption chiller is suitable for applications with a constant heat source, such as large commercial buildings and industrial facilities.
Indirect-fired absorption chiller: This kind of chiller uses an external heat source, such as a boiler or waste heat, to provide the necessary heat for the absorption refrigeration cycle without direct combustion. The indirect-fired absorption chiller has lower emissions and offers more flexibility in terms of heat sources. It is suitable for situations where combustion is restricted, like in urban areas with strict environmental regulations.
Some key specifications for absorption chillers include the following:
An absorption chiller's cooling capacity is measured in tons of refrigeration (TR). Larger models typically have a cooling capacity of dozens to hundreds of TR. The cooling capacity required for a specific application is determined by factors such as the size of the space to be cooled and the cooling demand.
The coefficient of performance (COP) of an absorption chiller is a key performance indicator. It indicates the ratio of the cooling capacity produced by the chiller to the energy input. The higher the COP value, the more efficient the chiller is at producing cooling. The COP of an absorption chiller is typically between 0.6 and 1.2, varying according to the model and working conditions.
An absorption chiller can provide different cooling capacities within a certain temperature control range. For instance, the chiller can provide a cooling capacity of 7.2 kW when the chilled water temperature is 7°C. The temperature control range is usually between 5°C and 20°C, and the cooling capacity changes with the chilled water temperature.
Maintaining an absorption chiller properly is essential to ensure its efficient operation and prolong its service life. Here are some recommended maintenance tips:
Business buyers should regularly inspect the absorption chiller's external components, including the heat exchangers, pipelines, and valves, looking for signs of corrosion, leaks, or blockages. If any issues are found, they should be repaired in a timely manner to avoid compromising the chiller's performance.
Water quality is critical to the proper functioning of an absorption chiller. Business buyers should maintain the quality of the water by routinely testing and adjusting the water's pH level, alkalinity, and hardness. Doing this reduces the risk of scale buildup or corrosion inside the chiller.
Business buyers should periodically lubricate the moving parts of the absorption chiller and clean the key components. When lubricating, use appropriate lubricants to ensure smooth operation of the moving parts. When cleaning, follow the manufacturer's instructions to avoid damaging the components.
Business buyers should perform major maintenance tasks, such as replacing key components or overhauling the unit, under the guidance of qualified professionals. Professional maintenance ensures the safety and reliability of the absorption chiller.
Industries such as food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical production require large-scale refrigeration for their operations and product storage. Theabsorption chiller can provide sufficient cooling for these commercial and industrial settings. In the food industry, absorption chillers are widely used in meat processing, dairy processing, and beverage production. Meat products need refrigeration to maintain their quality and safety. The low-temperature environment created by absorption chillers can ensure the freshness of meat. Dairy products such as milk and yogurt also need to be stored in low-temperature environments to prevent spoilage. Absorption chillers can help dairy processing companies maintain the quality and shelf life of their products.
In the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, absorption chillers can be used in the production process and to store chemical reagents and drugs at low temperatures. Many chemical reactions require specific temperature conditions, and absorption chillers can provide the necessary cooling to maintain the stable operation of the production process. Heat-sensitive chemical reagents and drugs are prone to chemical degradation and loss of efficacy at high temperatures, so they need to be stored in refrigerated spaces. Absorption chillers can create low-temperature environments to help preserve the stability and effectiveness of these substances.
The absorption chiller can also provide central air conditioning for large office buildings, shopping malls, and hotels. These places have a large flow of people, and central air conditioning systems must have strong cooling capacity to maintain indoor comfort. Absorption chillers can meet the cooling needs of these large spaces. The air conditioning industry also needs to install air-cooled absorption chillers. Air-cooled absorption chillers use outdoor air as the cooling medium, which can reduce energy consumption and operating costs.
Absorption chillers are used in power plants, petrochemicals, and other industries to provide cooling for key equipment such as generators, transformers, and process equipment. These devices generate a lot of heat during operation. Cooling is essential for them to operate normally and efficiently. Absorption chillers can provide stable and reliable cooling to these key devices, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the entire production system.
When considering purchasing an absorption chiller for a specific industry or project, several key factors should be taken into account to ensure the optimal solution is chosen.
It is essential to evaluate the full load efficiency of different absorption chillers. Pay attention to the coefficient of performance (COP) and energy consumption at full load. By choosing absorption chillers with high full-load efficiency, businesses can reduce operating costs and energy consumption.
Considering the partial load performance of the absorption chiller is also important. The COP value of the chiller at different load ratios and the control accuracy of the load are indicators that need to be focused on. Choosing an absorption chiller with good partial load performance can improve energy efficiency and stable operation in practical applications.
When selecting an absorption chiller, it is essential to consider the type and characteristics of refrigerants. Make sure that the refrigerants used by the chiller are suitable for the company's specific requirements and applications. Moreover, pay attention to the safety and environmental protection of refrigerants and ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
When choosing an absorption chiller, it is important to consider the machine's cooling capacity and scalability. Evaluate the business's current and future cooling load requirements, and select a chiller with the appropriate cooling capacity to ensure it can meet the company's demands for a long time. Also, consider the scalability of the chiller, allowing for easy expansion and adaptation to future needs.
When choosing an absorption chiller, consider its maintenance requirements and the availability of maintenance services. Choose a chiller with simple maintenance and reliable service support to minimize downtime and ensure system performance. Moreover, it is also important to read the manual and understand the maintenance procedures and requirements, and perform routine maintenance on the chiller as needed, so as to ensure the long-term efficient operation of the absorption chiller.
When selecting an absorption chiller, it is essential to evaluate not only the initial investment but also the life cycle cost. Consider the factors such as energy consumption, maintenance costs, and service life of the chiller, and choose a chiller with optimal performance and cost-effectiveness to ensure the long-term economic benefits of the business.
Q1: How does an absorption chiller work?
A1: The functioning of an absorption chiller is based on the cooling process, which can be divided into three main steps. In the first step, the absorption of a refrigerant (usually water) occurs in an absorbent solution. This results in a weaker absorbent solution and a saturated refrigerant being produced. In the second step, heat is applied to the saturated refrigerant, which then vaporizes. This process will then leave behind the absorbent solution or the concentrated lithium bromide. Finally, the vaporized refrigerant is then condensed back into a liquid state. It is then returned to the absorber, thus completing the cycle.
Q2: What are the advantages of absorption chillers?
A2: One of the major benefits of absorption chillers is their high energy efficiency. This is because absorption chillers use heat as their main driving force, rather than direct electricity. As a result, they consume less electricity and can be operated using various heat sources. Another advantage is that absorption chillers have a lower environmental impact. This is because they consume less electricity and produce lower greenhouse gas emissions than traditional compression chillers.
Q3: What are the common applications of absorption chillers?
A3: Absorption chillers are widely used in various industries and facilities that require large-scale cooling. Typical applications include commercial buildings such as hotels, shopping malls, and office buildings, as well as industrial facilities such as data centers, food processing plants, and manufacturing plants. Absorption chillers are also commonly used in district cooling systems, which provide centralized cooling services to multiple buildings and facilities in urban areas.