(12497 products available)














































































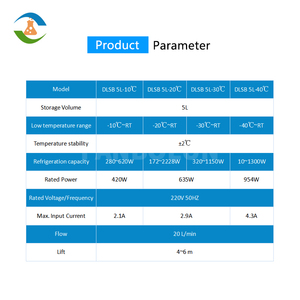


















































































































































Chillers are large industrial machines used to remove heat from a liquid via a vaporative process or heat absorption.
Absorption chillers:
Absorption chillers use heat to cool buildings. They absorb heat from the environment through a refrigerant cycle driven by heat rather than electricity. They are large, complex machines often used in central cooling plants for district cooling or to cool large commercial/industrial facilities.
Air-cooled chillers:
Air-cooled chillers are commonly found on rooftops or next to buildings. They use fans and ambient air to dissipate heat from the refrigerant in the cooling process. They are typically easier to install than water-cooled chillers since they do not require a cooling tower or specific condenser water piping.
Centrifugal chillers:
Centrifugal chillers are the most common type of chiller used in large cooling applications. They use a centrifugal compressor to compress refrigerant and transfer heat. Commonly found in large commercial/industrial buildings. They have high cooling capacities and are suitable for large spaces. They are efficient and often feature variable-frequency drives that allow the compressor speed to adjust according to real-time cooling demands, which also helps save electricity.
Water-cooled chillers:
Water-cooled chillers are typically used in larger commercial/industrial buildings that require more cooling capacity. They use water from a cooling tower to remove heat from a refrigerant through a heat exchanger. Water-cooled chillers tend to be more energy efficient than air-cooled chillers when cooling large quantities. However, they require a constant water flow from the cooling tower to function properly and efficiently.
Air-Cooled Chillers
They have huge fans that help to dispersing heat. The following table describes the specifications of them.
| Application | Industrial Plants, Commercial Facilities, Specialized Equipment |
| Cooling Capacity Range | 5 to 1,200 Tons / 20 to 4,200 kW |
| Typical Refrigerants | R-410A, R-134A, R-407C |
| Operating Temperature | -20 to 75 °C |
Water-Cooled Chillers
They use water to disperse heat generated during their cooling processes. The following table describes the specifications of them.
| Application | High-Heat-Removal Industrial Process, Large-Scale Air Conditioning |
| CpCooling Capacity Range | 10 to 2,500 Tons / 40 to 8,800 kW |
| Typical Refrigerants | R-123, R-134A, R-125/R-134A Blend |
| Operating Temperature | -20 to 50 °C |
| Condenser Types | Cooling Towers, Water Cooled Condensers |
Air cold chillers and water cold chillers need to maintenance constantly to keep effective working and prolong lifespan. Here are some essential maintenance tips.
Regular Cleaning:
Cleansing external surfaces, condensers, cooling fans and other radiators to remove dust, debris and contaminants. It help to maintain optimal heat dissipation and air circulation.
Lubrication:
Adding grease to water pump and cooling fan of chillers. It helps to keep smooth operation and reduce friction.
Components Inspection:
Checking whether are some problems of components. For example, leaks, damages, loose parts, abnormal noises or other issues. Users should repair or replace them if they find the problems.
Connection Inspection:
Users should inspect the refrigerant pipeline, water pipeline and electrical connections periodically. Besides, users should ensure there are no leaks, blocking or loose connections.
Industrial chillers play a really important role in lots of different industries. Here's how some key sectors use chillers:
When determining the price of a chiller, several factors first come into consideration before the customers or clients are even put into the equation. These are the capacities of the chillers, their sizes and dimensions, their cooling mediums, their types, the efficiencies of the chillers, their installation requirements, and, lastly, the brand and market.
Basically, everything about the chiller, what sets it apart from others, and what its functionalities are dictate its price. Its capacities, for example, range from small to high or large cooling capacities per unit. Naturally, larger capacity units will be higher in prices than others with lower capacities. The sizes and dimensions also impact the price since larger chillers typically have larger parts that require more necessary quantities to manufacture. Its cooling mediums also set it apart in pricing. As mentioned earlier, the water-cooled chillers are usually more expensive than air-cooled chillers due to their installations that require complex workings, only making sense through high efficiency.
The efficiency of coolers, as already stated above, can have a significant impact on the prices since high-efficient coolers do demand higher prices due to energy-saving features and operational costs.
Lastly, a significant price-setting factor is the manufacturer or brand and market. Chillres made by reputable brands or manufacturers will demand a higher price because they have a reputation to maintain, etc. Another example can be the market. Certain brands or manufacturers enter specific markets and are priced higher or lower depending on where they are being sold to.
When all of this is considered, buyers must also keep in mind that the price of the chiller must correlate with its performance. A high-quality chiller that works wonders might be worth investing in for a business that requires the chiller to be running at full capacity and high performance. A small start-up that requires a chiller for its premises that are not too high in demand can go for a more economical one.
Q1: What is the relationship between chillers' capacity and prices?
A1: The capacity of a chiller refers to its cooling power, typically measured in tons or kilowatts. Larger-capacity chillers are designed to cool more significant amounts of heat and are generally used in large commercial and industrial applications. Higher-capacity chillers usually have more giant and more efficient components and may have advanced technologies to optimize performance. Because of all these factors, chillers with larger capacities tend to cost more than smaller ones.
Q2: What are the market trends impacting chiller prices?
A2: The prices of chillers are affected by various market trends. One more crucial trend is the increasing demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions across several industries. Refrigerant conversion is another notable trend influencing the chiller market. Many manufacturers are replacing traditional refrigerants that affect the ozone layer.
Q3: How do the installation costs affect chiller prices?
A3: While cooling system prices are more significant, chiller installation costs are also significant. Businesses seeking to buy chillers usually consider all costs. Proper installation of the chiller is very important to ensure the machine performs at its best. This will require skilled labor, which will not come cheap. A poorly installed chiller may lead to increased operating costs and regular maintenance.