(16 products available)






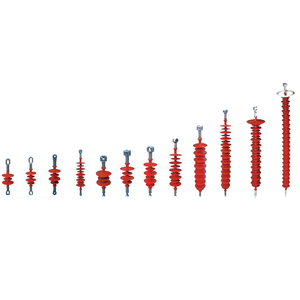

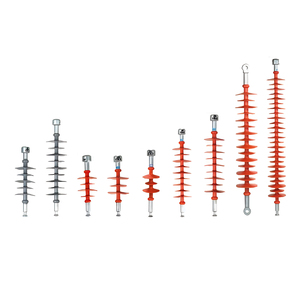





















Composite insulators are designed using non-ceramic materials like fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) as their support structure. They are widely used in high-voltage applications due to their lightweight construction, hydrophobicity, and resistance to environmental degradation. A composite insulator 230 KV is designed for 230 kilovolt applications, typically used in transmission lines. This voltage level is common in high-capacity power transmission across long distances. Several composite insulators exist in the market, each with different characteristics suited for various environments. They include the following:
Pin-type composite insulators
The composite insulator pin is designed with a core of high-strength material like fiberglass embedded in a resin. This is to ensure high strength and mechanical flexibility. The outer surfaces of all the FRP components are shaped in specific profiles. These profiles serve as the insulating surfaces. Regarding electrical functionality, this kind of insulator is very much similar to porcelain pin insulators. An insulator pin composite, however, has much improved performance characteristics. It provides enhanced electrical strength when in use in severe polluted environments.
Suspension-type composite insulators
Suspension composite insulators are probably the most common with regards to transmission lines. These are normally constructed with several insulator units strung together. This is done to form a flexible chain. The core is still made of FRP. However, the design usually incorporates a parabolic shape. This allows the insulator to suspend and consequently better absorb the load tension that is on the wire. In addition to this, the flexibility provided by the suspension-type insulator helps in reducing mechanical stresses. These insulators are therefore critical where long span applications exist.
Strain composite insulators
Strain composite insulators are tension devices. They are used to support the wire under high tension and stress. Installation points with heavy tension on the conductor require strain insulators to balance the load. Strain composite insulators are quite similar in construction to suspension insulators. However, they incorporate additional hardware. These additional features help distribute the mechanical load more effectively. The robust design of strain-type insulators gives cables additional support. This ensures they do not sag or break.
Post-type composite insulators
Post-type composite insulators can be found commonly in substation applications. These ones are installed vertically. Thus, they provide support for conductors and other electrical components. The design incorporates a long, cylindrical core made of FRP. The core is then covered with an elastomeric shed. The shed is helpful in providing the dielectric barrier. Post-type insulators are normally used to ensure that voltage is kept at bay. This is especially in the vicinity of electrical equipment such as transformers and switches.
Many people prefer silicone rubber insulators due to their minimal maintenance requirements. However, regular inspections are essential in extending their lifespan and working condition. Here are some of the maintenance and repair guidelines for a 230 kV composite insulator:
It is important to consider a few factors before purchasing 230KV composite insulators. These factors include the pollution level of areas where the client intends to install these insulators, mechanical loads, and span lengths. Below are some of the factors one should consider when purchasing these insulators:
Type of insulator
A suspension insulator should be used in long spans exceeding 300 meters. For spans that are less than 300 meters, a strain-type insulator is used. Lastly, a post insulator should be used in substations and switchgear.
Geographic and environmental factors
A point of installation's geographic and environmental conditions have a direct impact on the type of composite insulator one should purchase. Therefore, it's advisable to purchase insulators that are suitable for a client's local climate and geographical topography. For instance, areas that are prone to high humidity, salt, or dust require insulators with a high creepage distance. This is to prevent electrical trees from developing on the insulator surface. Likewise, potential hydrophobicity of the shed material used in the insulator is to enhance surface dryness.
Mechanical stresses and load
Mechanical load on the conductor is one of the key performance factors to consider when purchasing composite insulators. This is because the mechanical load directly influences the choice of electromechanical load of the insulator employed. High spans and heavy loads require insulators that have high electromechanical load.
Conductor characteristics
Standards recommend that manufacturers be selected based on the characteristics of the conductor being used in the installation. These characteristics include diameter, tension, and material type. They can, therefore, be obtained in different colors. One that depicts their effectiveness in supporting different conductors. In instances where the conductor is made of special material or has unique mechanical characteristics, customized insulators might be necessary.
Hydrophobicity
Hyrophobocity is mostly associated with the shed materials covering the insulator core. It is the ability to keep the insulator surface free from water under wetting conditions. A highly hydrophobic shed material is effective when used in areas that are prone to high levels of humidity and precipitation. One of the key factors that enhance hydrophobicity is the surface texture of an insulator. It should be relatively high and preferably made using microprotrusions.
Adherence to standards
It is prudent to ensure that the 230 kV composite insulator being purchased follows international standards and guidelines. These include IEEE, IEC, and ANSI. Manufacturer selection is best based on their strong reputation of consistency in delivering quality products. This is because these insulator types face quite a number of challenges. Some of them include long-term reliability, dielectric performance, and electrical flashover. Ensuring that one is using a standard-compliant product will eliminate a lot of these challenges.
A1: Composite insulators are basically non-ceramic insulator devices. They are made of solid insulating materials that are called hoods. These hoods are mostly formed using silicone rubber. Internally, they consist of a fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) rod and a terminating mass. Other materials used include electrical porcelain, glass, and other polymers.
A2: Composite insulators are preferred due to the low weight they come in with. That makes transporting and installing them easy. They are also preferred due to their high mechanical strength and flexibility.
A3: Composite insulators have an estimated lifespan of 30 years under normal conditions. However, this period can be longer or shorter depending on several factors. These factors include maintenance, environmental conditions, and pollution levels.
A4: Composite insulators are more effective than ceramic insulators in wet and dirty conditions. This is due to the hydrophobic nature that composite insulators have. These two types of insulators also differ in electrical and mechanical properties. While composite insulators have more mechanical flexibility and are lighter than ceramic insulators, ceramic insulators have better electrical performance than them.
A5: The pollution control strategy of composite insulators involves designing the shed profile to aid water droplet movement and minimizing surface contact. This helps in preventing pollution from being bridged electrically, which can lead to insulator failure. Manufacturers also ensure the silicone rubber used has a high hydrophobicity that helps in water repelling.