(2329 products available)



















































































































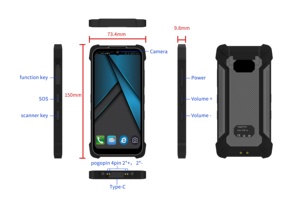




























Data management solutions are essential for organizations to effectively handle and utilize their data assets. They serve as systematic approaches and tools to ensure data integrity, availability, security, and accessibility across the enterprise. Various types of data management solutions address specific data needs, enabling organizations to derive meaningful insights and make informed decisions.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
DBMS is software that facilitates the creation and management of databases. It provides users and programmers with a systematic way to create, retrieve, and manipulate data. There are several types of DBMS, each catering to different data models and use cases. Relational DBMSs, such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, use tables to organize data and support SQL for querying. NoSQL DBMS, like MongoDB and Cassandra, handle unstructured or semi-structured data and offer scalability for big data applications. Hierarchical DBMS, such as IBM Information Management System (IMS), organize data in a tree-like structure, while network DBMS uses graph structures to represent relationships between data entities.
Data Governance
Data governance solutions ensure data quality, consistency, and compliance with regulatory standards. They establish policies, procedures, and standards for data management and define data ownership and accountability within organizations. Data stewardship is a critical component of data governance, where designated individuals or teams oversee data quality and integrity. Data quality tools monitor and cleanse data, ensuring accuracy and reliability. Data lineage solutions track the movement and transformation of data across systems, providing visibility into data flow and impact analysis. Compliance management tools ensure adherence to data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, by implementing data handling policies and audit trails.
Data Integration Tools
Data integration tools combine data from various sources into a unified view for analytics and reporting. Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) tools extract data from source systems, transform it to meet target requirements, and load it into a destination system, such as a data warehouse. Real-time data integration solutions enable continuous data synchronization across systems, ensuring up-to-date information. Data virtualization creates a logical view of data from multiple sources without physical data movement, simplifying access and reducing latency. API management facilitates data exchange between applications through well-defined APIs, enabling seamless integration and interoperability.
Data Storage Solutions
Data storage solutions provide the infrastructure to store and manage data at scale. Cloud storage services offer scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage and accessibility from anywhere. Object storage, such as Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage, stores data as discrete units called objects, making it suitable for unstructured data. Block storage, used in databases and applications, provides low-latency access to data blocks. Data warehouses are optimized for analytical workloads, enabling fast querying and reporting on large datasets. On-premises storage solutions, such as Network-Attached Storage (NAS) and Storage Area Networks (SAN), provide local data storage and management for organizations with specific compliance and performance requirements.
Data Security Solutions
Data security solutions protect data from unauthorized access, breaches, and loss. Encryption tools secure data in transit and at rest by converting it into unreadable formats for unauthorized users. Access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and identity and access management (IAM), restrict data access based on user roles and authentication. Data masking techniques obfuscate sensitive data elements in non-production environments, minimizing exposure to sensitive information. Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization through unauthorized channels. Backup and recovery systems ensure data availability and recovery in case of disasters, ransomware attacks, or accidental deletions.
Data Quality Management
Data quality management solutions address issues related to data accuracy, consistency, completeness, and timeliness. Data profiling tools analyze datasets to assess their quality and identify anomalies or discrepancies. Data cleansing solutions rectify errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies in data, ensuring a single version of truth. Data enrichment services augment existing data with additional information from external sources, enhancing its value. Data validation tools verify data against predefined rules or standards, ensuring adherence to quality benchmarks.
Master Data Management (MDM)
Master data management solutions create a single, coherent view of critical business entities, such as customers, products, suppliers, and locations. MDM establishes a central repository for master data and employs data matching, merging, and survivorship processes to eliminate duplicates and determine the authoritative source of truth. MDM governance frameworks define roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing master data, ensuring data stewardship and accountability across the organization. MDM implementation strategies address data harmonization, data model design, and integration with operational and analytical systems, enabling organizations to leverage consistent master data across applications and use cases.
Data Lifecycle Management
Data lifecycle management solutions govern data from creation to deletion, ensuring data relevance and compliance. Data retention policies define the duration data should be stored and align with legal and business requirements. Archiving solutions move historical data to lower-cost storage for compliance and audit purposes while minimizing the impact on active systems. Data minimization techniques reduce data volume by eliminating unnecessary or outdated data, reducing storage costs and compliance risks.
Data Analytics and Visualization Tools
Data analytics and visualization tools empower users to derive insights from data and present it meaningfully. Business intelligence (BI) platforms, such as Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView, enable interactive data visualization and dashboard creation, facilitating real-time monitoring and analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs) and trends. Self-service analytics tools democratize data access and analysis, allowing business users to explore data and create visualizations without relying on IT. Predictive analytics solutions leverage historical data and advanced algorithms to forecast future trends and behaviors, supporting proactive decision-making.
Below are the specifications and maintenance of data management solutions.
The Specification of Data Management Solutions
The following are the specifications for data management solutions:
1. Data integration: This specification enables users to combine and analyze information from several sources. It ensures that all data is accessible and complete for decision-making.
2. Data governance: This specification establishes rules and responsibilities for data ownership. It ensures that data quality, privacy, and security are maintained across the organization.
3. Data architecture: This specification outlines the design and structure of data storage and management systems. It ensures that data is organized and accessible efficiently.
4. Data quality: This specification focuses on maintaining high standards for data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. It ensures that the data used for analysis and decision-making is reliable.
5. Metadata management: This specification manages data about data, such as its source, meaning, and context. It helps users understand and utilize data more effectively.
6. Data security: This specification ensures that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access and breaches. It involves implementing measures like encryption and access controls.
7. Data storage: This specification addresses the capacity, performance, and cost of storing data in various systems. It ensures that data is stored efficiently and cost-effectively.
8. Data lifecycle management: This specification manages data from its creation to its deletion. It ensures that data is stored and maintained according to its relevance and value over time.
The Maintenance of Data Management Solutions
Below is the maintenance of data management solutions:
1. Regular updates and patches: Keeping the data management system up to date with the latest software versions, updates, and security patches is essential. This helps maintain optimal performance and protect against vulnerabilities.
2. Backup and recovery: Implementing a robust backup and recovery strategy is crucial. Regular backups of data should be taken to ensure data can be restored in case of loss or corruption.
3. Performance monitoring: Continuously monitoring the performance of the data management system is essential. This includes tracking data storage, processing, and retrieval performance to identify and address any issues promptly.
4. Capacity planning: Anticipating future data growth and managing capacity accordingly is crucial. This involves regularly assessing data management system resources to ensure they meet current and future data requirements.
5. Data quality management: Maintaining high data quality standards is essential. This involves implementing data quality processes, such as validation, cleansing, and enrichment, to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and completeness.
6. Security management: Regularly assessing and managing security risks in the data management system is essential. This includes implementing security measures, such as access controls, encryption, and monitoring, to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
7. Data lifecycle management: This involves managing data according to its relevance and value over time. It ensures that data is stored and maintained efficiently, optimizing storage resources and improving data management performance.
8. Compliance management: This involves ensuring adherence to relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards in data management processes. It includes implementing data privacy and security measures, such as data protection policies and practices, to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with legal requirements.
Choosing the right data management solution can be challenging. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a data management solution:
First and foremost, determine the budget and the cost of a data management solution for the organization. Some solutions may require a large budget for implementation and maintenance, while others are affordable.
Consider the scalability of the data management solution. Choose a solution that can grow and adapt to the organization’s changing needs and requirements.
Another factor to consider is the integration capabilities of the data management solution. Choose a solution that easily integrates with existing systems and tools in the organization.
Ensure that the data management solution has strong security features to protect sensitive data and comply with data protection regulations.
Select a data management solution that is user-friendly and easy to use. This will ensure that employees can quickly learn and adopt the system, reducing training time and increasing productivity.
Data management solutions should provide reliable technical support and customer service. This ensures that organizations can quickly resolve issues and get assistance when needed.
Data management solutions should provide organizations with analytical tools and reporting capabilities to gain insights from data and make informed decisions.
Data management solutions should be customizable to meet specific organizational needs and requirements. This allows organizations to tailor the system to their preferences and processes.
Lastly, consider the vendor's reputation and reliability. Choose a data management solution from a trusted and reputable vendor with a proven track record.
Here are some general steps for replacing a data management solution:
Assess data management needs
Evaluate the organization's data management requirements, including data volume, complexity, security, and compliance needs.
Identify a new solution
Research and select a new data management solution that aligns with the organization's needs. This could be a database management system, data warehouse, data lake, or another data management tool.
Create a migration plan
The migration plan will include a timeline, steps for data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL), data validation procedures, and a rollback strategy in case of issues during migration.
Prepare the new environment
Set up and configure the new data management solution. This includes hardware and software installation, security settings, data model design, and integration with existing systems.
Data mapping and transformation
Data from the old system is mapped to the new system. Data is transformed to meet the new system's requirements.
Data migration
Data is migrated using ETL tools or custom scripts. Data is extracted from the old system, transformed to match the new system, and loaded into the new data management solution.
Testing and validation
The data in the new system is validated to ensure accuracy and completeness. The functionality of the new data management solution is tested to ensure it meets the organization's requirements.
Training and documentation
Users and administrators are trained on using the new data management solution. Documentation is created for the new system's processes and configurations.
Go live and support
The new data management solution is implemented. Support is provided during the initial period to address any issues that may arise.
Q1: What are the key features of an effective data management solution?
A1: An effective data management solution should be scalable, secure, and provide data quality control. It should also ensure data compliance with regulations, offer data integration capabilities, and provide data accessibility and availability. In addition, it should have data governance features and support analytics and business intelligence.
Q2: What industries can benefit from data management solutions?
A2: Virtually every industry that deals with data can benefit from data management solutions. This includes sectors like finance, healthcare, retail, telecommunications, and manufacturing. For example, a vehicle parts data management solution can help companies manage data related to inventory, sales, and customer information.
Q3: How long does it take to implement a data management solution?
A3: The timeline for implementing a data management solution can vary based on several factors, including the complexity of the system, the size of the organization, and the readiness of the existing infrastructure. Typically, data management implementation can take a few weeks to several months.
Q4: Are data management solutions easy to use?
A4: Data management solutions are designed to be user-friendly, but the level of usability can vary depending on the complexity of the solution and the specific needs of the organization. Many solutions offer intuitive interfaces, data visualization tools, and user-friendly features to simplify data management tasks.
Q5: Can data management solutions handle big data?
A5: Yes, data management solutions are designed to handle large volumes of data, including big data. They provide scalable architectures, distributed processing capabilities, and advanced analytics features to manage and derive insights from big data effectively.
The web search volume for the keyword "data management solution" shows a significant upward trend, with an average monthly web search volume of 1,600. Over the past year, there has been a 46% increase in web searches, while the three-month change has surged by 116%. The data from the last 12 months reveals considerable fluctuations, ranging from a low of 590 web searches in March to a high of 3,600 web searches in July.
Analyzing the monthly web search volume data, "data management solution" experienced varied interest throughout the year. Starting with 1,300 web searches in December, there was a notable peak in January at 2,400 web searches, followed by a sharp decline in February to 1,000 web searches. The lowest point occurred in March with only 590 web searches, but there was a gradual increase leading up to July, where web searches almost tripled from the March figures. After July, the volume dropped back to 880 in August and September, before rising again in October and November to 1,300 and 1,900 respectively.
This pattern suggests seasonal influences and market dynamics affecting search behaviors. The spike in January could be attributed to new year resolutions and organizational drives, where businesses look to improve their data management practices. The sharp decline in February and March might indicate a post-holiday reduction in interest or budget constraints. The rebound in web searches from April to July aligns with the onset of fiscal planning for many companies, driving a renewed interest in efficient data management solutions. The subsequent dip in August and September could reflect a typical mid-year slowdown, followed by another uptick as companies prepare for year-end reviews and planning for the next year.