(35 products available)














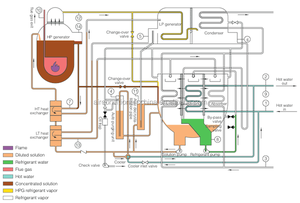

















































































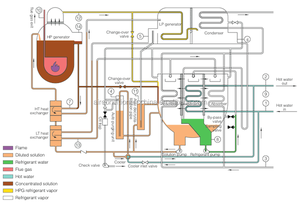

















A direct fired absorption chiller is a type of chiller that is used to cool water or other fluids by utilizing a heat source in the form of direct firing. Direct fired absorption chillers can be divided based on the type of refrigerant and the type of fuel used.
The most common types of direct fired absorption chillers are the water/lithium bromide (LiBr) chiller and the ammonia-water chiller. The water/LiBr absorption chiller is the most widely used direct-fired absorption chiller. It functions by absorbing water vapor into a lithium bromide solution. This process causes the remaining water to cool down. The ammonia-water absorption chiller is also a common type of direct-fired absorption chiller. It is suitable for applications that require lower temperatures than those supported by the water/LiBr chiller. It uses the ammonia-water combination as a refrigerant. The ammonia is then absorbed by the water in a generator, and the remaining water is then evaporated to produce cooling effects.
Direct-fired absorption chillers can also be classified based on the type of fuel they use, such as natural gas, propane, or dual-fuel.
The natural gas-fired absorption chiller is the most common type of direct-fired absorption chiller. It uses natural gas as the primary fuel source. Natural gas is burned in the combustor, and the hot flue gases generated are then used to drive the absorption refrigeration cycle. Another popular type of direct-fired absorption chiller is the propane-fired absorption chiller. It provides cooling services by burning propane gas. Propane is often used as a clean-burning fuel source. Propane-fired absorption chillers are widely used in areas where natural gas is not available. Dual-fuel absorption chillers are able to use two types of fuel sources, like natural gas and propane. Users can switch between different modes according to the actual situation. Dual-fuel absorption chillers provide users with more flexibility and adaptability.
The specifications of direct fired absorption chillers are as follows:
Generally, the cooling capacity is measured in tons or BTUs. The cooling capacity of a direct-fired absorption chiller is affected by the size of the flame, the amount of water absorbed, and the design of the unit. It is important to select a chiller that can meet its cooling load requirement while considering the chiller's capacity, which is typically between 100 and 2500 tons.
The flow rate refers to the rate at which the chilled water is circulated and is measured in gallons per minute. The flow rate of an absorption chiller is determined by the design of the internal components and the system. The flow rate must be able to meet the cooling demands of the system, such as the temperature required by the space being cooled and the cooling rate, which can vary depending on the time of year and the system used.
Direct-fired absorption chillers are highly efficient. The coefficient of performance (COP) is a measure of efficiency, which is the ratio of cooling to fuel input. The COP of a direct-fired absorption chiller can be as high as 1.7-1.9, which means it can produce 1.7-1.9 tons of cooling per unit of fuel. The efficiency of a direct-fired absorption chiller is affected by factors such as the temperature of the water entering the system, the design of the unit, and the maintenance of the unit.
Preventive maintenance is important for the long-term efficient and reliable operation of a direct-fired absorption chiller. It includes regular inspections and tasks performed by professional technicians. These include checking the burner and combustion system to ensure they are functioning properly and making any necessary adjustments, inspecting the absorption cycle and water loop to ensure there are no leaks or blockages, checking the control system and sensors to ensure they are accurate and reliable, and changing the filters and cleaning the components. The company's maintenance manual provides specific maintenance guidelines.
Direct-fired absorption chillers that use different types of fuels have different maintenance requirements. For example, the cleaning of the burner and combustion system may be different. It is important to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and consult a professional technician who is familiar with the specific type of direct-fired absorption chiller.
The direct-fired absorption chiller is widely used in various industries and fields, providing efficient cooling solutions in different scenarios.
In the manufacturing industry, an absorption chiller can cool down the production equipment and processes, such as cooling down the heat generated by the machinery and equipment during the production process.
Direct-fired absorption chillers are commonly used in large buildings, such as office buildings, hotels, shopping centers, etc., to provide central air conditioning and cooling for indoor environments.
In the food industry, direct-fired absorption chillers are used to cool and preserve food products, such as refrigerating storage rooms, freezers, and cold storage warehouses, to maintain the quality and safety of food products.
Direct-fired absorption chillers can be used in the energy industry for the cooling needs of power plants, especially in the power generation process. They can be used to cool down the equipment and guarantee the normal operation of the power plant.
In the medical and pharmaceutical industries, direct-fired absorption chillers are used in laboratories, pharmaceutical production, and medical facilities to keep the temperature at an appropriate level. It is to ensure the stability of the environment and the quality of drugs and experimental samples.
When comparing different types of absorption chillers, the following factors must be considered:
One of the main factors in choosing a direct-fired absorption chiller is the availability and cost of the heat source. Business buyers should assess their primary energy sources and costs, such as natural gas, propane, or oil, and then determine whether a direct-fired chiller is a cost-effective option for their specific situation.
Business buyers need to assess their building's cooling demand and choose a direct-fired absorption chiller with the appropriate capacity. The cooling capacity of chillers is typically measured in tons of refrigeration.
Direct-fired absorption chillers are generally larger than electric chillers. Business buyers need to determine whether their facilities can accommodate the space requirements for direct-fired absorption chillers and assess the installation complexity and cost.
Absorption chillers are generally more energy-efficient than electric-driven vapor compression chillers. Business buyers need to evaluate the energy efficiency of different models and choose a chiller with a high coefficient of performance (COP).
Consider the maintenance requirements and service availability of direct-fired absorption chillers when making choices. Understand the regular maintenance tasks, spare parts availability, and service support of different chiller brands to ensure the smooth operation of the system.
Q1: What kind of energy does an absorption chiller use?
A1: Mainly, direct-fired absorption chillers use heat energy to produce chilled water. However, different absorption chillers use various energy sources, including steam, natural gas, and water.
Q2: What are the advantages of a direct-fired absorption chiller?
A2: Direct-fired absorption chillers have several advantages. They are environmentally friendly, have low operating costs, and provide excellent scalability.
Q3: How does direct-fired absorption chiller work?
A3: The working principle of a direct-fired absorption chiller is to generate chilled water by using a refrigerant and an absorbent solution. Firstly, the refrigerant is evaporated using heat from the direct fire. The absorbed solution then absorbs the evaporated refrigerant, creating a solution. Finally, the absorbed refrigerant is heated to release the water that is reused in the air.