(5414 products available)

















































































































































































































M4 rivet nuts come in various forms, each intended for a specific purpose. Here are the most popular types of M4 rivet nuts.
Monel rivet nuts are manufactured from Monel metal, which is a mix of nickel, copper, and a small amount of iron, carbon, and silicon. Monel rivet nuts are highly resistant to various types of acids, alkaline substances, and salt. Therefore, they are often used in marine applications and in the chemical processing industry.
As the name suggests, these rivet nuts are manufactured from stainless steel. Stainless steel rivet nuts provide corrosion resistance and are extremely durable. In most cases, they are used in automotive, aerospace, and machinery applications.
Aluminum M4 nuts are highly regarded for their lightweight nature. They provide this at a low cost and offer decent corrosion resistance. These M4 nut rivets are often used in applications where weight reduction is crucial. For example, they are often used in the aircraft and electronics industries.
Copper rivet nuts possess excellent electrical conductivity and workability. However, they have low resistance to corrosion. They are often used in electronic applications, where these nuts are commonly used as threaded inserts.
These rivet nuts are generally used for applications where strength and load-bearing capacity are critical. They are often employed in heavy-duty industrial machinery, structural components, and construction equipment.
Here is a general procedure for utilizing M4 rivet nuts. This is in accordance with how they are conventionally used by many people.
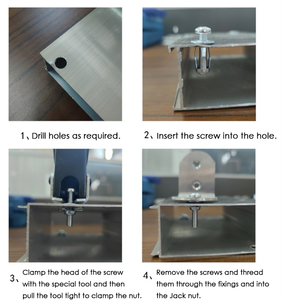
The first step in installing a rivet nut is to prepare the material where the nut will be embedded. This material can be any thickness ranging from 1mm to 3mm or a slightly thicker one. Then, a hole is drilled in the material that is slightly smaller than the diameter of the rivet nut.
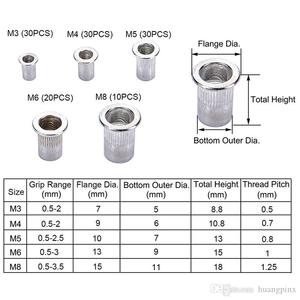
Once the hole is drilled, the M4 rivet nut is placed into the hole from one side of the material. The M4 nut can fit into a hole with a diameter ranging from 6mm to 7mm. An M4 rivet nut is a type of blind fastener that is designed to create a threaded hole in material.
Next, a rivet nut tool like a special rivet nut gun or an impact wrench is used to pull the mandrel. This causes the rivet nut's internal threads to expand and grip the back side of the material securely.
Once the rivet nut is set, the tool is detached from the mandrel. The mandrel is then trimmed off close to the rivet nut's surface. The rivet nut provides a strong threaded insert that enables easy assembly and disassembly of components.
In the end, when installed correctly, the M4 rivet nut creates strong, load-bearing threads on the exterior surface of the material. These nuts give users the advantages of a welded nut or a captured machine screw without requiring access to the interior side.
Maintaining and repairing M4 rivet nuts is vital for extending their lifespan and ensuring their performance remains at an optimal level. Here are some key maintenance and repair considerations.
Perform routine checks on the nuts and the installed rivet nut tool in structural components. This ensures users can catch any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage in good time. Look for stripped threads or physical deformation on the nut.
Clean the M4 insert nuts regularly. This prevents the build-up of debris, dirt, or corrosive substances. Use a soft brush or cloth with mild detergent and water. People should avoid abrasive materials that could scratch or damage the surface of the nut.
For rivet nuts used in areas with high humidity or exposure to chemicals, apply a light coating of anti-corrosive oil or lubricant. This offers an extra layer of protection. Choose stainless steel or Monel material for corrosive environments for Rivet nuts.
Over time, the attachment between the rivet nut and the bolt may loosen due to vibration or fluctuating loads. Check periodically and re-tighten as needed. If there is visible wear on either the nut or the bolt, replace the worn-out parts immediately.
If the M4 rivet nuts show signs of stripping or cracking, it may be necessary to repair or replace them. Damaged nuts should be removed using a tool designed for extracting rivet nuts. Repairing damage to a nut usually entails replacing a stripped or broken part.
Store M4 rivet nuts in a clean, dry environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use separate containers for the different materials to prevent cross-contamination.
M4 rivet nuts have a variety of customization options for buyers to choose from. Each of these options helps to meet specific application requirements. Here are some common customization options.
M4 nut rivets are manufactured from various materials that give them distinct properties. For example, they are often manufactured from stainless steel, aluminum, copper, or Monel. Each of these materials provides users with unparalleled resistance to corrosion and oxidation. They also give users strength and durability. Users could also choose to coat these materials with anti-corrosive coatings to increase their lifespan.
Users can also request various coatings on their M4 rivet nuts. For example, manufacturers often coat these coatings with zinc plating, which provides a barrier against rust and other forms of corrosion. Other coatings that manufacturers do are organic coating and chrome plating. These coatings often enhance chemical resistance and provide electrical insulation.
M4 rivet nuts have distinct head styles that give them different aesthetic and functional appeals. The most common are the flush head, standard head, and knurled head. Each of these styles offers a different level of load distribution and torque engagement. This makes them suitable for M4 nut bolt applications with varying surface requirements.
M4 rivet nuts are available in various grip ranges. This allows them to accommodate不同 material thicknesses like 1mm to 3mm. Manufacturers also customize this option according to the specific needs of their users. This ensures users have a flush finish on all their rivet nuts.
Manufacturers usually customize the thread diameter, length, or pitch of Rivet nuts to meet diverse application requirements. For example, some users may prefer finer threads for thin materials. At the same time, others may favor coarser threads for thicker ones. This provides greater load-bearing capacity.
The safety and quality of M4 rivet nuts are indispensable for several reasons. Here are some reasons why M4rivet nuts need to have good quality and safety.
The M4 rivet nut is designed with high-quality materials and undergoes stringent manufacturing processes to ensure enhanced load-bearing capacity. Stainless steel and Monel rivet nuts like M4 nuts are highly regarded for their unmatched tensile strength. The Rivet nuts provide excellent torque retention in high-stress applications. This makes them ideal for automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery usage.
Rivet nuts are often exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. Corrosion resistance thus becomes a critical safety factor. High-quality M4 rivet nuts are manufactured from stainless steel or Monel. These materials offer superior resistance to rust and chemical degradation. It, therefore, enhances the longevity of the nuts in adverse environments.
Good-quality M4 rivet nuts are engineered to withstand vibration and dynamic loads. Manufacturers achieve this by designing the nut's threads to provide a snug fit in the rivet hole. This ensures that the nut remains securely bonded to its installed material even under continuous vibration. It reduces the risk of loosening over time.
M4 rivet nuts that meet national and international quality standards like ISO and ASTM ensure safety and reliability. These standards regulate various factors. They regulate mechanical properties, material quality, and dimensions, ensuring the nuts perform as intended in critical applications.
M4 rivet nuts are primarily designed to spread loads over a larger surface area. This helps to reduce material fatigue and failure risks in the assembly. High-quality rivet nuts are engineered to distribute forces evenly across the installation surface. It, therefore creates a stable and secure connection for mounted components.
Manufacturers also focus on how easy the installation of M4 rivet nuts will be when considering quality and safety. They design the nuts for use with standard tools like pneumatic or hydraulic rivet nut guns. This promotes correct installation and significantly reduces the risk of damage to the nut, material, or surrounding components. It also ensures that users get a flush and aligned nut after their installation.
A1. Yes, people can use M4 rivet nuts with 3D-printed parts. However, the key consideration is ensuring that the material of the 3D-printed part is compatible with the M4 rivet nut. Manufacturers usually recommend embedding threads directly into the 3D-printed design. It provides a more robust anchor point for the rivet nut.
A2. Manufacturers make M4 rivet nuts from various materials. They commonly make them from stainless steel, aluminum, or copper. They do this to take advantage of the properties that each material offers. For example, they make stainless steel nuts for applications in corrosive environments. At the same time, they make aluminum nuts for applications where weight reduction is crucial.
A3.The M4 rivet nut tools employed in a rivet nut installation do not have adjustable torque settings. What these tools have are pressure-speed control mechanisms. These control the rate of nut setting based on how much load is applied by the user.
A4.M4 rivet nuts are not reusable after the nuts have been set in a completed assembly. Their reusability was made possible when manufacturers invented rivet stud removers. These removers allow for multiple usages of a single nut.
A5.M4 Rivet nuts are not commonly suitable for load-bearing applications in plastic components. This is due to the strength and gripping power that M4 nuts provide in metal materials. However, there are specific types of M4 nuts, like injection-molded rivet nuts, that are suitable for rivet nut guns intended for plastic components.