(16528 products available)









































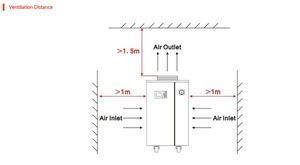














































































































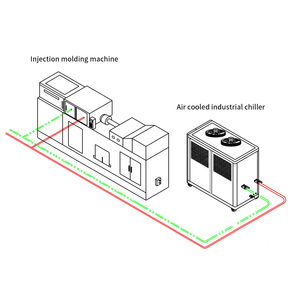




































A chiller is a machine that removes heat from a liquid through a vapor-compression or absorption cooling cycle. Chillers are usually used in large commercial and industrial facilities. There are mainly two ways to categorize chillers: the cooling method and the engine driving the cooling process.
More common classifications based on absorption and adsorption chillers are heat source/coolant transmission medium/working substance. For instance, absorption chillers are further divided into double-effect, single-effect, and lithium bromide/steam hybrids. Additionally, absorption chillers usually employ water as a refrigerant and heat from natural gas, steam, or hot water as the energy source to drive the cooling process.
Air-cooled chillers are perhaps the most popular kinds. Inside a mechanical room, a water-cooled chiller may be housed, typically covered, dusted, and somewhat widely exposed—to condensing units, cooling towers, or other equipment connected to the chiller via refrigerant piping.
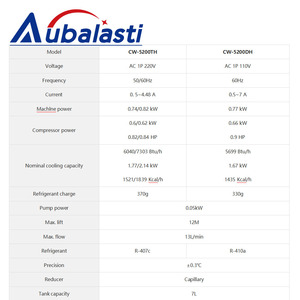
The main specifications to consider when buying an industrial chiller are the cooling capacity, outlet temperature, refrigerant, compressor type, voltage and power supply, as well as the size and weight of the unit.
Proper maintenance of a chiller can help prolong its lifespan and reduce operating costs. The following procedures are typically recommended:
Food processing industry
Food factories use chillers to cool food quickly, maintain food quality and freshness, and extend the shelf life of perishable items. Industries like meat and poultry, seafood, dairy, frozen goods, and bakeries are typical application scenarios where food processing chillers are used. For example, in the meat and poultry industry, chillers help maintain the optimal temperature during food processing, ensuring the quality and safety of products like chilled meat, poultry, and processed products.
Medical and healthcare industry
In the medical and healthcare industry, chillers are typically used in medical facilities like hospitals and clinics, as well as in pharmaceutical and biotechnology production. Hospitals need to use chillers to cool and maintain the temperature of medical equipment such as MRI machines, CT scanners, and X-ray machines. In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, chillers play a critical role in drug production, ensuring the proper temperature control of fermentation, reaction, and separation processes.
Manufacturing industry
In the manufacturing industry, different industries and fields use chillers to fulfill various specific duties. For instance, the plastic industry uses plastic chillers to cool and solidify plastic mold products, ensuring product quality and dimensional stability. Laser chillers are used to cool and maintain laser equipment's stability and performance; CNC machine tool chillers are used to control the processing temperature of CNC machine tools, ensuring machining accuracy and stability.
Transportation and logistics industry
Refrigerated carriers are vehicles equipped with chillers that provide refrigerated transport services to ensure the freshness and quality of perishable goods during transportation. Refrigerated containers are also equipped with a chiller to provide refrigerated storage and transportation services for goods at different ports and logistics centers, ensuring the supply chain's smooth and efficient operation.
Commercial industry
In commercial industries such as supermarkets, retail stores, restaurants, and cold storage, chiller play an essential role in preserving and displaying perishable goods. For instance, a supermarket uses a chiller to keep food like dairy products, meat, seafood, fruits, and vegetables fresh and maintain their quality. In restaurants, chillers preserve ingredients like meat, seafood, and vegetables to ensure food quality and safety.
When selecting chillers for industrial use, a number of aspects must be taken into account.
Cooling capacity:
It is imperative to match the chiller's cooling capacity with the particular application's cooling load. Analyze the variables that influence the cooling load, including heat-producing equipment, internal and external factors like the square footage of the area, insulation, the quantity of people, and any other pertinent elements. To guarantee optimal performance and efficiency, ensure the chiller has the appropriate cooling capacity to meet the demands.
Temperature control:
Consider the temperature range and precision required for the application. Select a chiller that can provide the necessary temperature control to maintain the desired cooling temperatures within the required range.
Energy efficiency:
To reduce operational expenses and environmental impact, choose a chiller with a high energy efficiency rating, such as an energy efficiency ratio (EER) or coefficient of performance (COP). Consider the chiller's integrated part's energy-saving technologies, such as variable-frequency drives (VFDs) and intelligent controls.
System compatibility:
Ensure that the selected chiller is compatible with the existing cooling system components, such as refrigerant, airflow, and infrastructure. Avoid potential integration issues or the need for extensive modifications.
Reliability and maintenance:
Opt for a reputable brand known for its reliable chillers. Consider the availability of maintenance services and spare parts to ensure timely support and minimize downtime.
Regulatory compliance:
Ensure that the selected chiller complies with environmental regulations and safety standards. Pay attention to the refrigerant's global warming potential (GWP) to minimize environmental impact.
Budget and life cycle cost:
Consider the initial investment cost, operating expenses, and maintenance costs over the chiller's lifespan. Perform a life cycle cost analysis to evaluate the total cost of ownership.
Q: What are some trends in the chiller market?
A: The chiller market is moving towards smarter technology, with more machines having chillers connected to the Internet for easy management. Also, there is a big focus on energy-saving machines as more industries aim to reduce their energy use and carbon footprint. More chillers are using natural refrigerants like ammonia or CO2, which are less harmful to the environment.
Q: How do chiller orders work?
A: Businesses looking to buy chillers in bulk typically start by contacting the chiller manufacturer or supplier directly. They can discuss their needs, quantities, and any specific features required for the chillers. After this, the business will usually get a quote for the order, including the price, delivery time, and any additional fees. If the business agrees with the terms, they will place the order, and a contract might be signed. A deposit will likely be required to cover some of the production costs upfront.
Q: Which is more important, the chiller’s condenser or evaporator?
A: Both the evaporator and condenser in a chiller are crucial for its operation. Chillier functions depend on the proper performance of both parts, which allow the refrigerant to absorb heat from the liquid being cooled and release that heat into the atmosphere or a cooling water system.
Q: Are all chillers noisy?
A: No, not all chillers are noisy. While some larger, older models may produce more noise, most modern chillers are designed to operate quietly.