(806 products available)





























































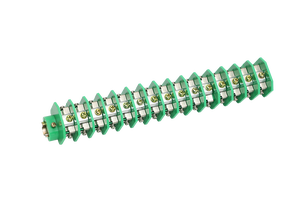


















































































































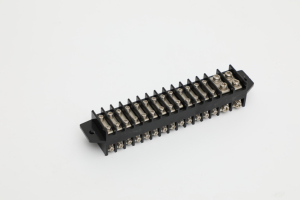










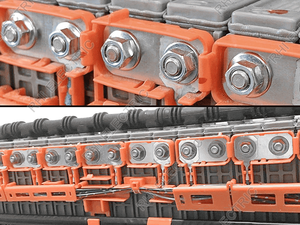
Small busbars refer to a conductive material that's either insulated or uninsulated, where the uninsulated conductive material is called the busbar assembly, and the insulated one is simply referred to as the insulated busbar system. They're mostly used in electrical distribution systems.
These are some of the most common types of small busbars available on the market:
Rigid busbars
Rigid busbars are stiff electrical conductors usually made from copper or aluminum with squared or rectangular profiles. These characteristics make them ideal for transporting large currents where flexibility isn't a necessity. Their rigidity gives them an advantage during installation, especially in systems where components are at a fixed position. In addition, their sturdy structure makes them easier to manufacture since it's mostly done using extrusion or machining processes.
The common application areas for rigid busbars include power distribution in industrial manufacturing, commercial electrical systems, and high-voltage power grids. They are also popularly used in metal perforated busbar boards where they distribute large power to various devices on the unit.
Flexible busbars
Unlike rigid busbars, flexible busbars can be bent or shaped to fit specific designs or configurations. They're mostly made from thin metal sheets or a blend of copper and aluminum foil, which is then plated with either copper or aluminum. Their flexibility makes them ideal for use in tight spaces or where equipment is required to move, for instance, in vibrating machinery. Common areas of application are dynamic equipments like elevators and conveyors, or operating equipment that produces a lot of heat, which can lead to expansion and contraction.
Insulated busbars
Insulated busbars feature a dielectric coating on the surface intended to eliminate the need for additional insulation measures. Insulated busbars can be in either rigid or flexible forms, although they're mostly rigid. The insulation protects from electrical shorts and lets the busbars be positioned closer together, thus offering more power in a compact design. Aside from electrical insulation, the coating also helps protect against corrosion. They're commonly found in low-voltage electrical distribution systems like switchgear, cabinets, and control panels.
Composite busbars
Composite busbars combine features of both insulated and uninsulated busbars. They're designed to maintain high-current capacity, and the areas with close proximity to one another are insulated to prevent electrical shorts, while the low-density regions that are far apart are left uninsulated to allow ease of electrical connection. This configuration allows for higher current densities in compact spaces. Typical applications are switchgear and high-performance power distribution systems.
Small busbar materials have a direct impact on their durability and performance. Here are some of the materials that small busbars are made of:
Copper
Copper is one of the most preferred materials when manufacturing a busbar since it has excellent conductivity. Copper busbars are compact, making them ideal for high-current transfers, with the added benefit of being more resistant to corrosion and thus increasing its longevity in an electrical environment.
Aluminum
Aluminum is a great conductive material that's less dense than copper, making the busbars lighter in weight. While its conductivity is lower than copper, the investigation shows that using larger aluminum busbars offers comparable performance at a lower price. Corrosion resistance is another characteristic of aluminum busbars, especially in environments with high humidity or where water is a concern.
Steel
In cases where mechanical strength or structural support are more of a concern than electrical conductivity, stainless steel or galvanized steel are the go-to materials for busbars. While steel has less conductivity compared to copper or aluminum, it comes in handy in situations where rigidity and durability are more critical.
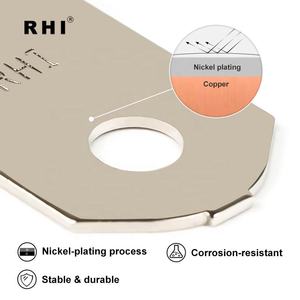
Nickel
Nickel has good corrosion resistance properties and decent conductivity, and that's why it's commonly used for coatings on other busbar materials, especially in environments where corrosion could lead to degradation or loss of conductivity over time. For example, aircraft, marine, and chemical plants use nickel busbars.
Titanium
Titanium is one of the most electrically conductive materials with high corrosion resistance properties. Though it has lower conductivity compared to copper and aluminum, titanium busbars are extremely durable. Its corrosion resistance helps maintain conductivity over time and thus makes it ideal for harsh environments. Its high strength also makes it well-suited for applications where mechanical robustness is a priority. Common areas where titanium is used include chemical processing, marine environments, and aerospace power systems.
Galvanization
Galvanization entails applying a zinc coating to a copper or aluminum busbar to protect it from corrosion, especially in environments with high humidity or exposure to moisture. The zinc acts as a sacrificial layer that corrodes before the underlying metal, thus extending the lifespan of the busbar. It's commonly used in outdoor installations or industrial facilities where moisture levels are high.
Nikotec coating
Nikotec coating involves applying a nickel-based alloy to busbars to improve conductivity, especially for composite busbars. The coating provides excellent corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and a wear-resistant surface which makes it beneficial for high-demand electrical applications. Commonly found in power distribution systems, renewable energy installations, and areas where corrosion could otherwise impact performance.
Copper plating
Copper plating applies a layer of copper to a busbar made of another material, usually aluminum. This provides the conductivity benefits of copper while using a lighter, more economical substrate. The coating also offers corrosion resistance to the underlying material. Copper plating comes in handy in applications where power density is critical, like data centers, telecommunications equipment, and electric vehicle charging stations.
Chromate conversion coating
This is a corrosion-resistant chemical treatment applied to copper or aluminum busbars. It creates a thin, protective layer that helps prevent oxidation while maintaining good electrical conductivity. It's often used in military and aerospace applications where corrosion resistance is vital, as well as in electronics and automotive systems.
Industrial power distribution
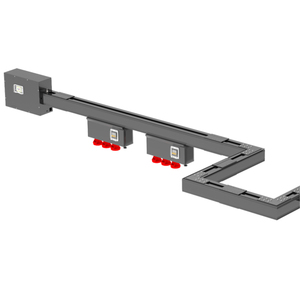
Manufacturing facilities heavily use small busbars in power distribution systems to transfer electricity from main supply lines to equipments and machinery. This helps ensure that critical operations continue to receive the necessary power. Besides, busbars offer a centralized solution for distributing large electrical currents efficiently throughout an expansive industrial setup. They're also helpful in managing the heavy electrical loads that are usually associated with industrial machinery. This means that machinery receives reliable power without the risk of overloads or fluctuations. Busbars are also easier to install and maintain, which improves operational efficiency. They help reduce downtime since the maintenance of the power distribution system is simpler compared to traditional wiring. In addition, small busbars improve safety since they're enclosed systems that minimize the risk of electrical shock or shorts.
Data centers
Small busbars serve a critical role in power distribution and redundancy in high-performance data centers. They help efficiently distribute large electrical currents from main power sources to numerous servers and equipment. By centralizing power distribution, busbars enable easier management of electrical loads, reduce cable clutter, and improve space utilization. Busbars also increase system reliability by providing redundant power paths to critical equipment.
Commercial buildings
In large commercial buildings or office complexes, small busbars distribute electrical power throughout the structure from a main switchgear or transformer. This helps offer a streamlined method of supplying power to lighting systems, heating and cooling equipments, and other electrical devices. Since they're more space-efficient, busbars help minimize the amount of cabling that needs to be routed throughout the building. They also enhance installation since they're easier to configure and deploy compared with extensive wiring systems. In addition, small busbars increase safety by reducing the risk of overloaded circuits and electrical hazards. Their enclosed design helps prevent electrical shorts and provide better protection from exposed conductors.
Renewable energy systems
Small busbars are used in solar power systems to collect and distribute electricity generated from photovoltaic panels. They also play a key role in energy storage systems like batteries by facilitating power flows between components. Busbars help manage and distribute the electrical output from multiple panels back to the inverter and eventually into the power grid or building. They enable the integration of more panels into a system without sacrificing performance. Since they have a lower resistance, busbars help minimize energy losses. Also, their robust design means they can handle high currents from large solar arrays. Plus, they help reduce installation costs by simplifying the wiring setup. In battery systems, busbars connect battery cells to inverters and other components to enable efficient energy storage and retrieval.
Current carrying capacity
Determine the amount of electrical current the busbar will be required to handle. This is crucial since going for the right size can avoid overheating and ensure safety. To do this, calculate the total current load of the electrical system, then consult the manufacturer to find the recommended current capacity, and see which one of them can accommodate the load. Remember that ambient temperature affects current capacity, so consider the environment when taking the measurements.
Material
As mentioned, busbars are mostly crafted from either copper or aluminum, so it's advisable to go for one that matches alloying with other components in the system. Copper is more compact and has better conductivity, while aluminum, though less effective, is lighter and more cost-efficient. In cases where mechanical strength is a primary concern, steel busbars are more suitable.
Size and form factor
Usually, a larger surface area means better heat dissipation and performance. Also, a greater thickness and width will mean increased current capacity. Although smaller sizes are more space-efficient, they're not as effective. Go for the size that best fits the installation specifics while considering current capacity as well. It might be tempting to pick a smaller size since it will be more adjustable during installation, but in the long run, that will affect performance. Instead, pick a size that's more practical, and if space is a struggle, get a more efficient solution like a compact busway system.
Insulation and safety measures
There are some insulated busbars that offer additional safety measures, especially in high-voltage systems. They reduce the risk of electrical shorts, but insulated busbars are more expensive. Consider the application environment. For instance, insulated busbars are ideal for areas that require operators' access, while uninsulated busbars, though more practical, are suitable for controlled environments. Also, confirm that the insulation materials are compatible with the working conditions. For example, certain extreme conditions demand more durable insulating materials.
Installation ease
Go for the busbars that are easy to install since that will help save both time and labor costs. Check for features like mounting brackets, pre-drilled holes, or flexible configurations, especially if the installation space is tight. Also, look for lightweight materials since they won't need heavy lifting during the installation process.
A1. Busbar systems are electrical power distribution frameworks that use busbars to quickly transfer electricity from one point to another within an installation. They can handle higher current loads, require less space than traditional wiring, and simplify installation and maintenance. Due to these benefits, they're commonly used in industrial plants, commercial buildings, data centers, and other high-power settings.
A2. Busbars work by providing a low-resistance pathway for electrical currents to flow from power sources like transformers or generators to various loads throughout a facility. Since they're constructed from conductive materials like copper or aluminum, they can efficiently manage large currents and quickly distribute them across an electrical system.
A3. The first benefit is improved reliability. Busbars handle high power density, reducing the risk of overloads or circuit failures. Then there's increased safety, since they're enclosed systems that cut down electrical shorts and shocks. The fact that they're easy to maintain and monitor also improves their reliability. Thirdly, there's better thermal performance as well as increased design flexibility, power redundancy, volume, weight, and installation simplicity.
A4. Busbars are more preferable because they handle higher power levels, require less space compared to traditional wiring, and provide installation and maintenance ease. They also improve system reliability. What makes them indispensable, though, is their capability to manage increased current loads, making them ideal for extensive commercial and industrial applications.