(68 products available)



















































































































































































A steam absorption chiller is a complex machine with many types. The following table summarizes the common types:
Cooling capacity
Cup, the cooling capacity is the first specification to be noted. It indicates how much heat the chiller can absorb from the environment. This is typically indicated in tons or kilowatts (kW). One ton equals 3.517 kW of cooling.
The temperature range at which the chiller can operate.
Absorption chillers are designed for specific evaporator temperatures. The lower evaporator temperature will allow more heat to be absorbed, resulting in greater cooling. A standard absorption chiller has an evaporator temperature range of 0 to 10 degrees Celsius.
Chiller efficiency
Absorption chiller efficiency is indicated by the coefficient of performance (COP), which is the ratio of heat removed to the energy used to remove heat. This is the ratio of the cooling energy produced by the chiller to the thermal energy supplied to drive the cooling process.
The refrigerant used in the chiller.
Absorption chillers use water as a refrigerant. Unlike compression chillers, which use artificial refrigerants like R-134A, R-410A, R-22, or R-404A, water is a natural refrigerant occurring in nature. This makes water ideal for large-scale cooling applications like industrial processes, air conditioning, and refrigeration.
Classical versus LiBr absorption chillers
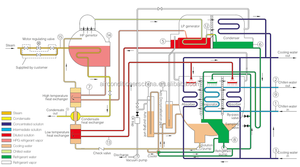
Some absorption chillers are classified as lithium bromide (LiBr) or ammonia (NH3) cooling systems. LiBr is only applicable to water generators. Classical water absorption cooling works by evaporating water from the evaporator. The water vapor then travels into the absorber, where lithium bromide takes the water vapor. NH3 works differently by absorbing refrigerant ammonia into an absorber with a high heat exchanger. The ammonia condensate will then re-inject into the evaporator to start the whole refrigeration process again.
Absorption chillers need regular maintenance to ensure they work well, stay efficient, and last a long time. Following this maintenance schedule can help prevent breakdowns, cut repair costs, and extend the machine's life.
Every day:
Weekly:
Turn off the power supply while doing inspections. It is also very important to take the entire absorption chiller machine into account. A whole machine maintenance concept is important. All parts of a chiller machine are related.
Some chemical substances or changing concentrations of solutions may cause corrosion to occur in the ammonia absorption chiller. Temp and chemistry tech are crucial. It is important to understand the corrosion mechanism for accurate and precise machine component maintenance.
Regular cleaning is also very important. Debris and dirt will pile up and hinder the efficient heat exchange process, which is the fundamental working principle of an absorption chiller. Thus, condenser, evaporator, and cooling coils need to be cleaned regularly.
Absorption chillers are useful in a variety of sectors. Here are some typical applications of absorption chillers:
HVAC systems
Large plants, offices, and hotels use steam absorption chillers as a cooling source for their central HVAC systems. Benefiting from their high capacity and efficiency, they ensure the whole building is at a suitable temperature and environment.
Process cooling
The chemical industry, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and other manufacturing industries require constant cooling. Steam absorption chillers are suitable for providing the stable and constant cooling that is necessary for those processes.
Industrial Refrigeration
Steam absorption chillers can be used as a cooling system in industrial refrigeration. It is suitable for cold storage, refrigerated warehouses, and mechanical refrigeration systems.
Co-Generation and Tri-Generation Systems
Co-generation systems simultaneously produce electricity and useful heat. Tri-generation systems produce electricity, heat, and chilled water. Both of the systems can utilize steam absorption chillers to convert excess heat into coolness, thus improving the overall energy utilization efficiency.
Heating and Cooling Networks
Steam sources can come from centralized heating facilities, power plants, or industrial sites. They can be transmitted to different locations through piping systems. Once they arrive at the destination, absorption chillers can convert the steam into cold energy to meet localized cooling demands.
Marine Applications
Steam absorption chillers have the potential to be used in marine applications like ships and offshore platforms. On these occasions, they can be employed to cool the living quarters, equipment, or other spaces on the ships, thereby ensuring the comfort and safety of the personnel and the normal operation of the equipment.
Steam absorption chillers are usually efficient, quiet, and dependable. The major consideration when selecting a steam chiller is knowing its requirement and matching them with the features of the chiller.
Cooling requirement:
Users should define their cooling requirements in terms of load capacity (in kw), temperature range, and operating conditions. Perform a detailed load calculation to determine the appropriate capacity of the absorption chiller.
Available heat source:
Determine the type and quality of the steam or hot water available at the installation site. Consider factors such as pressure, temperature, and quantity. Ensure compatibility between the chiller and the heat source.
Efficiency and performance:
Users should compare the energy efficiency ratio (EER) and annual fuel utilization efficiency (AFUE) of different absorption chiller models. Select a chiller that offers high energy efficiency and performance to minimize operating costs and environmental impact.
System integration:
Consider the absorption chiller's ability to integrate with other systems, such as heating equipment, control systems, and distribution networks. Ensure proper coordination and compatibility to achieve optimal overall system performance.
Space and installation requirements:
Check the dimensions and weight of the absorption chiller to ensure it fits in the available installation space. Consider the installation method and required clearances for proper maintenance and operation.
Regulatory compliance:
Ensure the selected absorption chiller complies with relevant standards and regulations. Consider the chiller's environmental impact and refrigerant type to meet sustainability goals.
Q1: What is the steam absorption chiller cycle?
A1: The absorption chiller works in a closed loop. It starts with the refrigerant evaporating in the cooling space. The evaporation process absorbs heat, making the refrigerant low-pressure vapor. The vapor moves to the absorber, where it mixes with the absorbent. The mixture is called a solution. The solution then gets pumped into the generator. In the generator, heat from the steam source raises the temperature of the solution. The heat increases the pressure of the refrigerant, causing it to separate from the absorbent. The refrigerant is now a high-pressure gas. It moves into the condenser, where it releases heat to the outside environment and changes back into a liquid. The liquid refrigerant goes back into the evaporator, and the cycle starts again.
Q2: What is the difference between absorption and compression chillers?
A2: The main difference between absorption and compression chillers is how they move heat. Compression chillers use electricity to power a mechanical compressor that compresses the refrigerant. On the other hand, Absorption chillers depend on heat to drive the cooling process and use an absorber, generator, pump, and lithium-bromide-water cycle to function.
Q3: What kind of steam does a steam chiller use?
A3: In the context of steam absorption chillers, the term "steam" refers to water vapor or humidity resulting from boiling water. It is different from industrial high-pressure steam. A steam absorption chiller can work with low-pressure steam from a central boiler or high-pressure steam from an industrial process.
Q4: What is the efficiency of absorption chillers?
A4: The efficiency of absorption chillers can vary based on factors like the design of the chiller, how well it is maintained, the operating conditions. But their efficiency is generally lower than that of compression cooling systems. The cooling effectiveness of absorption chillers is measured by a coefficient of performance (COP). The COP of absorption chillers typically ranges from 0.6 to 1.4.