(946 products available)








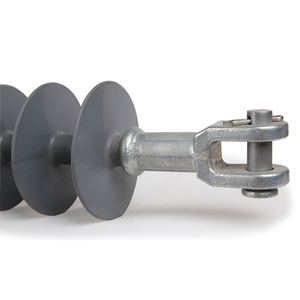



















































































































































A straining insulator is a device used in electric transmission and distribution lines. It is a tension insulator that supports a wire and withstands the wire's tension. Straining insulators are usually placed at the pole or tower top. They help maintain the wire's stability and strength. There are several types of straining insulators:
String insulator
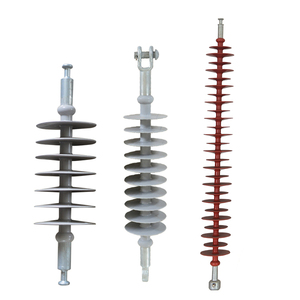
A string insulator is a series of insulator discs connected to each other by a metallic wire. It can be made from ceramic material and is used in high-voltage transmission lines. The insulator discs are connected to each other using metallic fittings. The number of discs can vary depending on the voltage requirement. The string insulator has both mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties. It can withstand high voltage and is used in long-distance power transmission. One of the main advantages of a string insulator is that it can be easily installed and maintained. It is also less expensive than other types of insulators. However, ceramic string insulators are more brittle and can be easily damaged. They also have a lower mechanical strength compared to other types of insulators.
Suspension insulator
Suspension insulators are used in overhead transmission lines to insulate conductors from towers or poles. They are made up of multiple insulator units connected together by metallic links. The design allows the insulator to hang from the supporting structure, resembling a pendulum. This type of insulator can withstand high voltage and is commonly used in long-distance power transmission lines. The main advantage of suspension insulators is their ability to withstand high mechanical stress and voltage. They are also easily replaceable and can be easily installed. However, suspension insulators are more expensive than other types of insulators, and they are also larger and heavier, making them less suitable for certain applications.
Strain insulator
Strain insulators are used in overhead power lines to withstand wire tension. They are large ceramic insulators designed to resist both electrical voltage and mechanical stress. Strain insulators are typically installed at the ends or bends of transmission lines, where they help maintain the stability and integrity of the wire. Strain insulators are essential for maintaining the stability and integrity of overhead power lines. They are used in both AC and DC power lines and are designed to withstand both electrical voltage and mechanical stress.
Tension insulator
Tension insulators are used in overhead power lines to maintain wire tension. They are designed to withstand both electrical voltage and mechanical stress. Tension insulators are typically used at the ends or bends of transmission lines. They help maintain the stability and integrity of the wire. Tension insulators are essential for maintaining the stability and integrity of overhead power lines. They are used in both AC and DC power lines and are designed to withstand both electrical voltage and mechanical stress.
Straining insulators have a specific design to meet the requirements of high-voltage power transmission lines.
Material:
Insulators are made from a material called porcelain. It is a very strong and hard material. It can also be glass or polymer. These materials do not let electricity pass through them. They are very good at insulating. They help keep the high voltage wires safe and prevent electricity from escaping where it should not.
Shape:
Porcelain insulators have a shape like a giant mushroom. The top part, called the cap, is flat and wide. The middle part is thick and has a few grooves or ridges. The bottom part is again flat and wide. This shape helps insulators work well. The insulator stays on the wire. The grooves make it stronger against being pulled or strained. It also helps the insulator hold up against bad weather. The wide top and bottom parts keep water and dirt from getting on the wire. If water or dirt got on the wire, it could cause problems. But the tall, thin middle part helps keep the electricity from getting out where it shouldn't. The taller distance makes it harder for electricity to jump out.
Insulating Material Properties:
The materials used for insulators have special properties. They have a very high melting point, much higher than the temperatures they would ever reach even in very hot weather. This keeps them from melting in the sun. The materials are also very hard. That keeps them from breaking easily if something hits them. They do not conduct heat well. That means even if a lot of electricity goes through the wire, the insulator stays cool. They can handle a huge amount of electrical voltage without any problems.
Straining insulators are used in various industries and applications requiring electrical insulation and mechanical tensioning. One of the primary applications of straining insulators is in overhead power transmission lines. These insulators are installed on transmission line towers to support and insulate the energized conductors from the tower's metallic structure, which could cause electrical grounding. Straining insulators in overhead power transmission lines ensure that the conductors can withstand tension forces from the tower's construction and help maintain the lines' stability and safety.
Another important application area for straining insulators is in communication lines. Overhead communication lines, such as telephone and internet lines, require straining insulators to provide similar support and insulation as seen in power transmission lines. These insulators ensure that the conductors carrying communication signals remain insulated from the supporting structures, thereby preventing any electrical faults that may disrupt communication.
Stringing insulators are commonly used in railways. Insulated wires are used in electric railways to provide support and tensioning for the electrified railway system. Straining insulators ensure that the overhead contact lines, which supply electric power to trains, are properly insulated from the supporting masts. This insulation is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of electric trains, as it prevents any electrical leakage that could harm passengers or damage railway equipment.
Moreover, straining insulators find use in various industries where overhead wiring systems are employed. For instance, in street lighting systems, electric wires are suspended overhead to light up roads and sidewalks at night. Straining insulators provide support and insulation for these overhead wires, ensuring they operate safely without any risk of electrical faults. Similarly, industrial applications involving overhead wiring also utilize straining insulators for their insulated conductors.
Performance Requirements:
Determine the performance requirements for the straining insulator. Consider factors such as voltage level, mechanical load, environmental conditions, and installation location. This will help identify the specific type and size of insulator needed.
Material Selection:
Choose the appropriate materials for the straining insulator based on the application and environment. Common materials include porcelain, glass, epoxy resin, and other polymer composites. The material selection should consider factors such as electrical performance, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature resistance.
Design and Standards:
Ensure that the design of the straining insulator complies with relevant industry standards and specifications. Consider factors such as electrical performance, mechanical strength, insulation performance, and dimensional requirements. Consult industry standards and guidelines to ensure the design is safe and reliable.
Testing and Quality Assurance:
Conduct testing and quality assurance for the straining insulator. Perform electrical tests, mechanical tests, insulation tests, and environmental tests to verify the performance and reliability of the insulator. Ensure that the product meets the design requirements and industry standards before it is put into use.
Manufacturing Process:
Choose appropriate manufacturing processes and techniques for producing straining insulators. This may involve processes such as material molding, surface treatment, assembly, and quality inspection. Ensure that the manufacturing process is efficient and the product quality is consistent.
Supply Chain and Procurement:
Establish a supply chain and procurement process for straining insulators. Identify reliable material suppliers and component manufacturers. Ensure the timely supply of materials and components to support the production schedule. Consider factors such as cost, quality, and delivery time when procuring.
Installation and Maintenance:
Provide instructions and guidelines for the installation and maintenance of straining insulators. Ensure that the proper installation procedures are followed during the installation to ensure the insulator's performance and reliability. Regularly inspect and maintain the insulator to ensure its long-term stable operation.
Q1. What are the benefits of using straining insulators?
A1. One advantage is that they can withstand heavy loads and high voltage, ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. They also offer excellent electrical insulation, helping prevent short circuits and other electrical failures. Additionally, these devices are resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, extreme temperatures, and chemicals, making them suitable for use in harsh conditions.
Q2. How do one install and maintain straining insulators?
A2. To install a straining insulator, secure the conductor within the insulator's grooves using the provided clamps or fittings, and then attach the insulator to the supporting structure using appropriate hardware. Regular inspections for signs of wear or damage, ensuring the integrity of the conductor's attachment to the insulator, and cleaning the insulator to remove accumulated debris or contaminants are essential for proper maintenance.
Q3. What are the industry standards and regulations for straining insulators?
A3. Various international standards, including IEC and ANSI, specify performance requirements, testing methods, and design guidelines for straining insulators to ensure their safety and effectiveness in supporting and insulating conductors.