(82214 products available)







































































































































































Cold Vulcanizing
Cold vulcanization is a chemical process that uses a special adhesive that contains hardeners and accelerators. This adhesive bonds the patch to the tire and ensures the surfaces being repaired are bonded. The process of cold vulcanization is simpler compared to hot vulcanization. This is because the repair technicians do not have to heat the tires or use any equipment that generates heat. Additionally, the risk of damaging the tire's internal structure is eliminated. As a result, cold vulcanization is a preferred method for repairing small tears and punctures. In cases where the damage is more extensive, cold vulcanization may not be effective.
Hot Vulcanization
Hot vulcanization is a process that uses heat and pressure to create strong bonds between the rubber surfaces and the rubber compound being repaired. During this process, the repair technician uses a rubber repair material that is similar to the rubber on the tire. The technician then applies heat to the material using a heated metal plate. The heat causes the rubber in the material to transform into an elastic state, which allows it to bond with the tire's rubber.
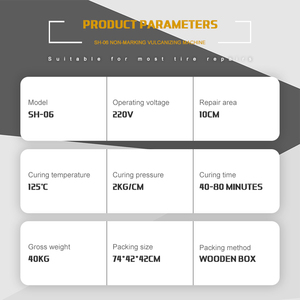
Different tires have different specifications for the vulcanization process. However, some common factors affect the vulcanization process:
The type of rubber
Natural rubber is often preferred for tire manufacturing. It provides good elasticity and wear resistance. Synthetic rubber is also used. It is more resistant to abrasion and chemicals.
The type of curing agent
Sulfur is the most commonly used curing agent for tire rubber. It is added to the rubber compound before mixing. Other curing agents like peroxides are used for high-performance tires. Peroxides give better heat and aging resistance.
The temperature and time of curing
Tires are cured in large molds called molds. The molds give the tire its final shape and tread pattern. Curing is done in hot presses. The presses heat the rubber to the required temperature. The temperature is maintained throughout the curing period.
The type of tire
Different types of tires require different vulcanization specifications. For example, passenger car tires have lower curing temperatures than truck tires. This is because truck tires experience more stress and higher operating temperatures.
For vulcanization to be successful, all these specifications must be carefully controlled. This ensures that the tires have the desired properties. This improves performance, safety, and durability. Proper tire vulcanization is important for optimal tire performance.
Vulcanization is a critical process in rubber tire manufacturing. It enhances the properties of the rubber. This makes the tires wear-resistant, heat-resistant, and durable. To maintain the properties achieved through vulcanization, the following are some maintenance practices that should be observed:
Wholesale buyers should consider the following factors before purchasing any vulcanizing products:
Product Quality
Buyers should first consider the quality of vulcanizing products before anything else. The quality of vulcanization products determines the effectiveness and durability of the repairs. Premium quality goods have a tendency to give consistent performance while lowering the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Furthermore, high-quality items inspire confidence in their customers. Buyers may draw in a devoted clientele that relies on the effectiveness of premium goods.
Supplier Reliability
Buyers should find trustworthy suppliers with a reputation for on-time deliveries and high-quality products. Consistent availability of products is made possible by establishing relationships with reliable suppliers, which also reduces inventory shortages. Furthermore, trustworthy suppliers stand by their products and offer assistance in the event of flaws or issues. Buyers can address product problems with the help of the supplier's support.
Product Range
Buyers should select suppliers who offer a wide variety of vulcanizing goods to meet various audiences and needs. Different car models and tire sizes call for various patching methods and adhesive combinations. Buyers may cater to various customer segments and increase their market reach by investing in a wide product range. Furthermore, a varied product offering enables buyers to take advantage of emerging trends and innovations in the industry.
Cost and Profitability
Buyers should evaluate the cost and profit margins of vulcanization products. To maximize profitability, they should strike a balance between product quality and competitive pricing. Furthermore, buyers should consider the long-term viability of vulcanization products. They should invest in products that are cost-effective and provide reliable performance over time, reducing the need for repeated repairs.
Safety Standards
Buyers should ensure that vulcanization products adhere to established safety standards. Products that meet safety requirements reduce potential risks during the repair process and ensure the safety of both technicians and customers. Furthermore, compliance with safety standards protects buyers from legal liabilities and enhances their brand reputation.
Ease of Use
Buyers should consider the practicality and efficiency of vulcanization products. For instance, quick-curing adhesives save time and increase productivity, while self-vulcanizing patches reduce the need for additional equipment. Products that are easy to apply and require minimal training for technicians help reduce errors and ensure consistent repair quality.
Customer Reviews
Buyers should conduct research to gather feedback from end customers about the performance and reliability of vulcanization products. Positive reviews and recommendations from end customers can help buyers make informed decisions and select products that have a proven track record.
Vulcanization is important in the rubber industry. It improves the strength and elasticity of rubber. The process combines sulfur with rubber using heat. This creates cross-links in the rubber molecules. As a result, the rubber becomes more durable.
Rubber vulcanization is important in tire repairs. It makes the patches strong and flexible. This ensures the repaired area lasts long. The vulcanization process in tire repairs involves: Applying a repair material to the damaged area. This material can be a patch or a bead of repair rubber. The repair material contains sulfur compounds. Heating the repaired area. This helps the repair material bond with the tire rubber. The heat causes the sulfur compounds in the repair material to fuse with the tire rubber. This process creates a strong, flexible bond. It ensures the repaired area has similar properties to the rest of the tire.
Businesses involved in tire repairs can benefit from vulcanization. It enhances the quality and durability of tire repairs. To carry out the process, they need vulcanization equipment. This includes a vulcanizing machine, repair materials, and heating elements. Proper training ensures the vulcanization process is done safely and effectively.
Here is how to DIY vulcanizing rubber repair:
Prepare the surface
Clean the rubber surface. Remove contaminants like dirt, oil, and moisture. Use a wire brush or sandpaper. Roughen the surface. This helps the adhesive bond. Roughen the surface. This helps the adhesive bond.
Cut the patch
Cut a patch from rubber material. Ensure the patch is larger than the damaged area.
Apply adhesive
Apply a thin layer of vulcanizing adhesive. Use a spatula or brush. Spread it evenly. Let it dry for a few minutes.
Prepare the patch
Roughen one side of the rubber patch. This helps the bond form. Apply a thin layer of vulcanizing adhesive. Spread it evenly. Let it dry for a few minutes.
Assemble the vulcanizing tool
Follow the manufacturer's instructions. Connect the heating element to the timer and temperature controller.
Vulcanize
Place the vulcanizing tool over the patched area. Set the timer and temperature. Follow the manufacturer's instructions. Apply pressure. Secure the vulcanizing tool with clamps or weights.
Cool down
Once the vulcanization time is complete, remove the heat. Allow the patched area to cool down.
Inspect
Check the patch for cracks or bubbles. Ensure it is well-adhered. Inspect the patch for cracks or bubbles. Ensure it is well-adhered.
Test
Reinflate the tire. Check for air leaks. Visually inspect the patch. Ensure there are no bubbles or gaps. The patch is well-adhered to the rubber material. Conduct a pressure test. Ensure the patch maintains the tire's air pressure.
Q1: How long does the vulcanization process take?
A1: The vulcanization process can last from a few minutes to several hours. This depends on the type of rubber being used and the thickness of the rubber component that is being vulcanized.
Q2: What are the benefits of vulcanization?
A2: Vulcanization makes rubber stronger. It increases its resilience to heat and its ability to resist abrasion. This increases the lifespan of rubber products.
Q3: What is the difference between vulcanization and non-vulcanization?
A3: Non-vulcanized rubber stays soft and pliable. It has a sticky feel to it. This type of rubber is often used in sealants and adhesives. It cannot be molded into any shape. On the other hand, vulcanized rubber is molded into shapes and is used in tires, shoes, and industrial products.